Mr. Igor Radulovic defended his BSc thesis on computer vision and machine learning for creating a prediction model for sign language. The defence took place on 3 October at UDG. This effort was inspired by the AI4S3 course and was supported by mentors from NCC Montenegro and HPC4S3ME team.
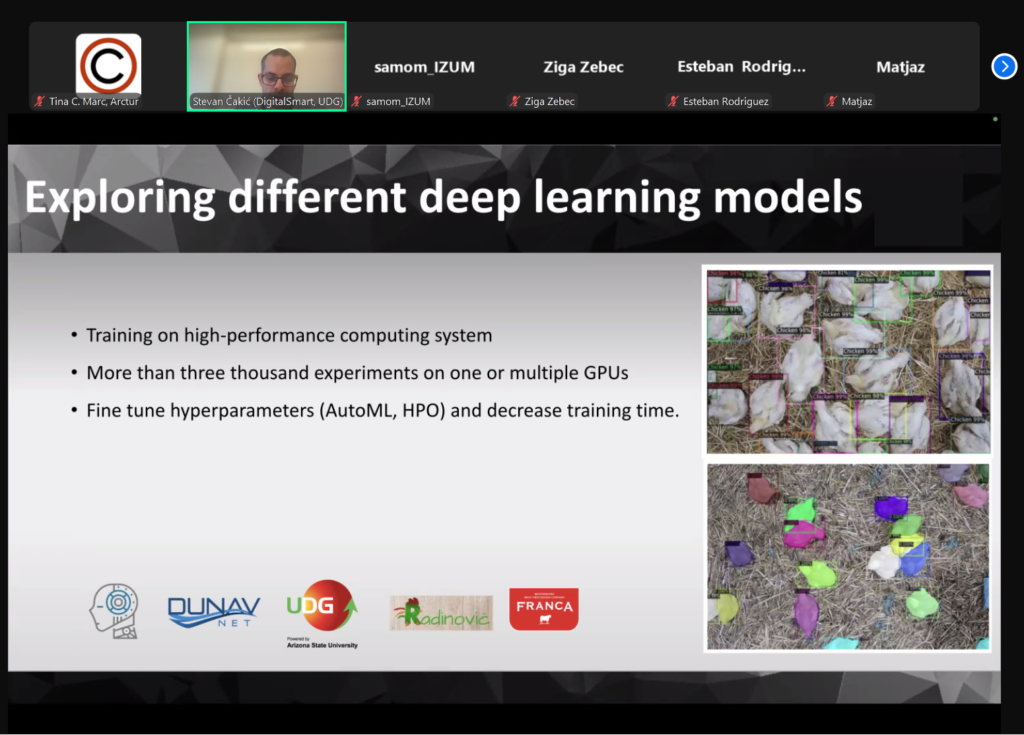
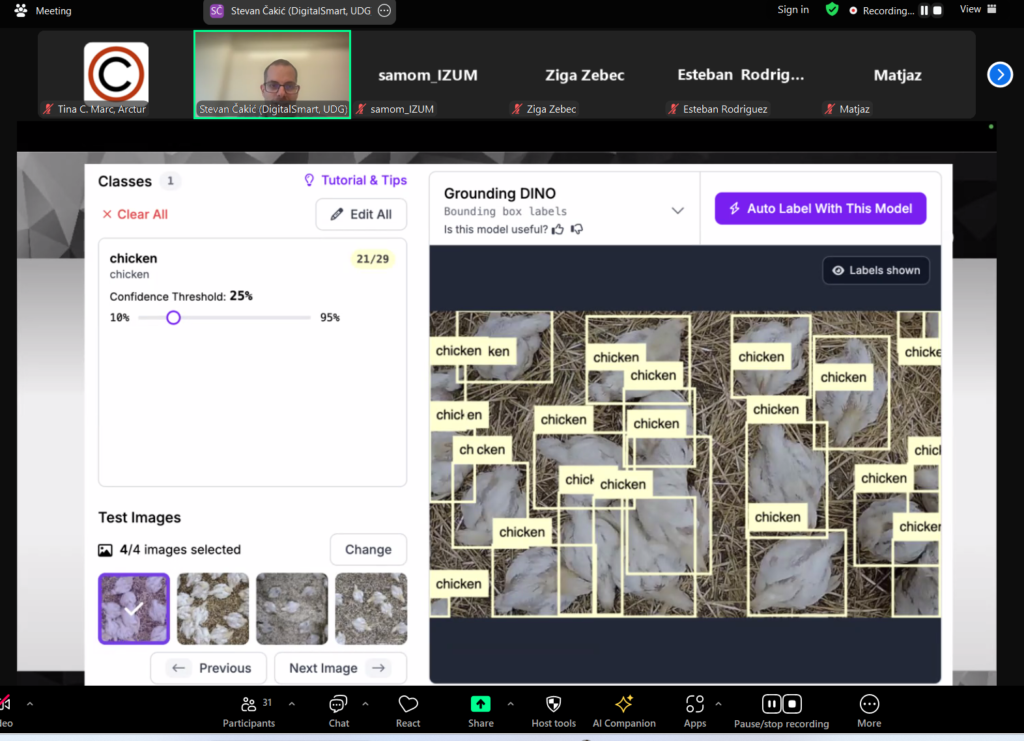
ABSTRACT – This thesis explores the use of advanced computer vision and machine learning techniques to develop a system that enables the translation of sign language into speech or written text in real time. The project aims to facilitate the communication of deaf-mute people with people who do not know sign language, in order to overcome language barriers and improve the social status of deaf-mute people in society. Using technologies such as Google Colab, Python, Roboflow, VS Code and Detectron2, a system was developed that recognizes various American Sign Language (ASL) gestures and converts them into understandable information. The system is based on deep neural networks and processes such as model training and instance segmentation, in order to achieve a high level of accuracy and reliability. Through the evaluation of the results, an impressive performance of the model was achieved with an F1 result of 95.6%, while the challenges in the technical limitations remained an important point of future development. This work points to the significant social impact of the application of computer vision in the communication of deaf and mute people, enabling them to integrate and be present in modern society.